Machine Learning vs AI What’s Actually Different
Discover the key differences between machine learning and artificial intelligence. Learn how AI and ML work together, their unique applications.

Artificial intelligence and machine learning are terms frequently used interchangeably in today’s technology landscape, yet they represent distinct concepts with different scopes, methodologies, and applications. This confusion often leads organizations astray when selecting the right technology for their specific business needs. The critical differences between AI vs machine learning are essential for anyone seeking to leverage these transformative technologies effectively.
The relationship between AI and ML is more interconnected than hierarchical. While machine learning is a subset of AI, not all artificial intelligence systems rely on learning mechanisms. Artificial intelligence represents the broader umbrella concept—any computational system designed to exhibit human-like intelligence—while machine learning focuses specifically on algorithms that improve through data exposure and experience. Think of AI as the entire field of intelligent machines, whereas ML functions as one primary method within that field. This distinction matters significantly for implementation strategy, resource allocation, and realistic expectations about system capabilities and limitations.
The global market for AI and machine learning continues to expand rapidly, with organizations across healthcare, finance, retail, and manufacturing investing heavily in these technologies. By their differences, business leaders and technologists can make informed decisions about which approach best serves their organizational goals. This comprehensive guide explores the nuances of machine learning vs artificial intelligence, examines their practical applications, and clarifies when each technology proves most valuable.
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
- Artificial intelligence refers to computer systems explicitly designed to mimic and replicate cognitive human functions such as reasoning, learning, problem-solving, and decision-making. AI systems accomplish complex tasks that historically required human intelligence by utilizing mathematical models, logic frameworks, and rule-based systems to simulate how humans think and act.
- AI technology encompasses multiple approaches beyond pure learning. Rule-based systems, expert systems, and knowledge-based frameworks enable machines to make intelligent decisions without necessarily learning from data. For instance, a chess-playing program using predetermined strategies doesn’t learn but still demonstrates artificial intelligence through logical reasoning and strategic execution. AI applications range from simple automated systems to highly sophisticated solutions that interact naturally with humans.
The scope of artificial intelligence is remarkably broad. AI capabilities include natural language processing for human communication, computer vision for interpreting images and videos, robotics for autonomous physical tasks, and speech recognition for voice commands. AI systems can function autonomously or semi-autonomously, making decisions and executing tasks with minimal human supervision after initial programming.
Artificial intelligence’s primary goal centers on creating intelligent systems capable of performing diverse cognitive tasks, solving multifaceted problems, and delivering human-like reasoning across various domains. Whether deployed in customer service chatbots, medical diagnostic systems, or autonomous vehicles, AI-powered systems represent humanity’s effort to extend intelligent capabilities beyond biological limitations.
What is Machine Learning (ML)?
Machine learning constitutes a specialized subset of artificial intelligence focused explicitly on enabling computational systems to learn patterns, extract insights, and improve performance through data exposure. Rather than relying on explicit programming instructions, ML systems develop predictive models by analyzing historical data and identifying statistical relationships.
The fundamental principle underlying this involves feeding algorithms large quantities of data, allowing these ML algorithms to discover patterns independently, and subsequently applying learned insights to new, unseen data. This data-driven approach eliminates the need for programmers to anticipate every possible scenario; models adapt and evolve as they encounter new information.
- Machine learning technology has emerged as the dominant implementation method for artificial intelligence because ML algorithms demonstrate superior flexibility, scalability, and adaptability compared to traditional rule-based systems. Modern AI implementations predominantly leverage techniques because of their demonstrated effectiveness across diverse industries and complex problem domains.
- ML capabilities span classification tasks (categorizing data into predefined groups), regression analysis (predicting continuous numerical values), clustering (identifying natural data groupings), and anomaly detection (flagging unusual patterns). Machine learning models now power email spam filters, recommendation engines, fraud detection systems, and medical imaging analysis tools, all working without explicit programming for each specific scenario.
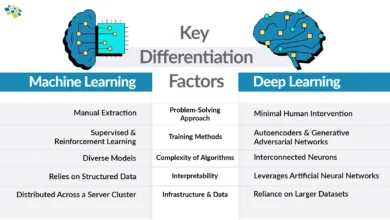
Key Differences Between Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence
Scope and Breadth
The most fundamental distinction between AI and ML concerns their conceptual scope. Artificial intelligence represents an expansive field encompassing any technology enabling computers to replicate human intelligence, including robotics, rule-based systems, natural language processing, computer vision, and expert systems. Focuses narrowly on developing algorithms and statistical models that learn from data to generate predictions or make autonomous decisions.
Consider AI vs ML through this lens: all is artificial intelligence, but not all artificial intelligence involves. A deterministic rule-based system demonstrating logical reasoning constitutes artificial intelligence despite containing no learning mechanism whatsoever.
Learning Mechanisms
The approaches diverge significantly regarding how systems acquire and utilize knowledge. AI systems can operate through multiple mechanisms: explicit rule definition, knowledge representation, logic-based reasoning, or data-driven learning. Traditional artificial intelligence methods often involved expert human knowledge manually encoded into systems.
Machine learning algorithms, by contrast, inherently depend on learning from data. ML models improve automatically as they process additional training data, without human-directed rule updates. Supervised learning approaches utilize labeled training data, while unsupervised learning identifies patterns within unlabeled datasets, and reinforcement learning optimizes behavior through environmental feedback.
Problem-Solving Approach
- Artificial intelligence solutions typically follow predetermined logical pathways established during system design. These systems execute programmed strategies consistently, handling scenarios their designers anticipated explicitly or that fall within defined rule parameters.
- Machine learning systems demonstrate greater flexibility by adapting their approach based on observed data patterns. Instead of following static rules, ML models continuously refine their predictive accuracy through data analysis. This adaptability makes machine learning particularly effective for complex environments where predefined rules prove impractical or incomplete.
Implementation Complexity
- Implementing artificial intelligence often requires subject matter experts, data scientists, and engineers collaborating to define rules, encode knowledge, and establish system logic. Initial implementation can be straightforward, but maintaining accuracy as circumstances evolve becomes challenging without continuous manual updates.
- Machine learning implementations demand substantial initial data collection and computational resources for model training. However, once trained, ML models adapt automatically to new data patterns, reducing long-term maintenance burdens compared to rule-based AI systems. The operational complexity differs significantly from traditional artificial intelligence approaches.
How Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence Work Together
Rather than viewing machine learning vs artificial intelligence as competing technologies, modern systems typically integrate both approaches. Machine learning has become the dominant implementation method for artificial intelligence because ML algorithms effectively enable AI systems to achieve intelligent behavior at scale.
Contemporary AI-powered systems predominantly employ techniques as their foundation. Natural language processing models are used to understand and generate human language. Computer vision systems leverage deep learning, a specialized machine learning subset, to recognize objects, faces, and patterns within images. Recommendation engines on Netflix, Spotify, and Amazon employ machine learning algorithms to deliver personalized content matching user preferences.
Deep learning, which represents an advanced machine learning approach utilizing artificial neural networks, has powered most modern artificial intelligence breakthroughs. By combining multiple techniques, AI developers create increasingly sophisticated systems demonstrating remarkable human-like capabilities.
Machine Learning Types and Algorithms
Machine learning categories clarify how ML systems approach different problem types and utilize various learning techniques.
Supervised Learning
Supervised machine learning trains algorithms on labeled datasets containing both input data and corresponding correct answers. ML models learn relationships between inputs and outputs, subsequently predicting outcomes for new, unlabeled data. Supervised learning approaches power classification tasks (email categorization, image recognition) and regression problems (sales forecasting, price prediction).
Common supervised learning algorithms include decision trees, support vector machines, neural networks, and gradient boosting methods. These techniques dominate practical applications because labeled training data enables precise model development.
Unsupervised Learning
- Unsupervised machine learning discovers hidden patterns within unlabeled data, requiring no predetermined answers or guidance. ML algorithms identify natural data groupings, correlations, and structural relationships independently. Applications include customer segmentation, image compression, and anomaly detection.
- Unsupervised learning approaches like K-means clustering and hierarchical clustering prove valuable when data labeling proves expensive or impractical. Machine learning systems employing unsupervised techniques extract surprising insights from raw, unstructured data.
Reinforcement Learning
Reinforcement trains agents to optimize behavior through environmental interaction. Systems receive rewards for desirable actions and penalties for undesirable ones, gradually learning optimal strategies. Reinforcement learning algorithms power game-playing AI systems, autonomous vehicle navigation, and robotic manipulation tasks.
Real-World Applications: AI and Machine Learning in Action
Healthcare and Medical Diagnostics
Machine learning models analyze medical imaging data—X-rays, MRIs, CT scans—identifying tumors, abnormalities, and disease indicators often matching or exceeding human radiologists’ diagnostic accuracy. AI-powered systems predict patient health risks, recommend personalized treatment protocols, and accelerate drug discovery by identifying promising molecular compounds. Machine learning applications in pathology, radiology, and cardiology demonstrate extraordinary potential for earlier disease detection.
Financial Services and Fraud Detection
Financial institutions deploy machine learning algorithms for real-time fraud detection, identifying suspicious transaction patterns instantly. AI systems analyze spending behavior anomalies—unusual geographic locations, atypical purchase amounts, unexpected transaction timing—flagging potentially fraudulent activities. Dramatically reduces false positives while catching legitimate threats, protecting millions of customer assets daily.
E-Commerce and Personalization
Machine learning recommendation systems analyze purchase history, browsing behavior, and preference patterns to suggest products matching individual customer interests. Amazon, Alibaba, and other e-commerce giants employ sophisticated machine learning algorithms, generating billions in incremental revenue through personalized product recommendations. AI-driven recommendation engines continuously refine suggestions as ML models learn from user interactions.
Natural Language Processing and Virtual Assistants
Artificial intelligence systems like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant leverage technology to understand spoken commands, interpret context, and formulate natural responses. Natural language processing algorithms, a specialized machine learning domain, convert human communication into computational instructions. Chatbots powered by machine learning handle customer service inquiries, schedule appointments, and provide intelligent assistance without human intervention.
Autonomous Vehicles and Robotics
Self-driving vehicles integrate multiple machine learning models for simultaneous tasks: recognizing lanes and pedestrians, predicting traffic behavior, planning navigation routes, and avoiding obstacles. Deep learning, an advanced machine learning approach, processes camera and sensor data, enabling autonomous decision-making. Robotics applications are increasingly accomplishing manufacturing, logistics, and service tasks with increasing precision.
Benefits and Advantages of AI and Machine Learning

Automation and Efficiency
Both artificial intelligence and automation dramatically reduce human effort by automating repetitive, time-consuming tasks. AI systems handle scheduling, data processing, and routine decision-making. Machine learning models continuously improve efficiency as they process more data, requiring minimal human oversight once deployed.
Data-Driven Decision Making
Machine learning algorithms analyze vast datasets, extracting actionable insights that inform strategic decisions. Predictive analytics, powered by machine learning, forecast market trends, customer behavior, and operational risks with impressive accuracy. AI-driven analytics transform raw data into competitive advantages.
Enhanced Accuracy and Consistency
Machine learning models eliminate human error, cognitive biases, and inconsistency, delivering reliable results across millions of transactions or decisions. AI systems maintain perfect accuracy performing specialized tasks, never experiencing fatigue or distraction, unlike human workers.
Scalability and Cost Reduction
Once deployed, machine learning systems handle exponentially increasing workloads without proportional cost increases. AI automation reduces labor expenses, accelerates processing timelines, and improves organizational capacity.
Limitations and Challenges
Data Requirements
Machine learning models demand substantial training data for effective performance. Supervised learning requires laboriously labeled datasets. Data quality, consistency, and representativeness profoundly impact outcomes. Insufficient or biased data compromises ML model accuracy.
Interpretability Issues
Complex systems, particularly deep learning neural networks, function as “black boxes”—humans struggle to understand why ML models make specific predictions. This opacity creates challenges in healthcare, finance, and legal applications where explainability is critical.
Computational Demands
Machine learning training requires substantial computational resources and energy. Deep learning model development demands powerful GPUs or specialized processors, limiting accessibility for smaller organizations.
Maintenance and Drift
Machine learning models degrade as real-world data distributions shift from the training data. Model drift necessitates continuous monitoring, retraining, and updates, ensuring sustained performance—ongoing operational expenses are often underestimated during initial implementation.
The Future of AI and Machine Learning
- Artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies continue evolving rapidly. Emerging developments include transfer learning, enabling knowledge reuse across different tasks, federated learning training ML models while preserving data privacy, and AutoML platforms automating model development.
- Generative AI, a specialized machine learning subset, creates original content—text, images, code, audio—from minimal prompts, revolutionizing creative and technical fields. Large language models like ChatGPT demonstrate capacity for sophisticated language and generation.
As these technologies mature, organizations increasingly recognize that artificial intelligence and machine learning integration drive sustainable competitive advantage. Rather than viewing AI and ML as separate choices, forward-thinking enterprises deploy both complementarily—leveraging machine learning’s data-driven adaptability alongside artificial intelligence’s broader cognitive capabilities.
More Read: Data Quality Management for Machine Learning Success
Conclusion
The distinction between machine learning and artificial intelligence ultimately reflects scope versus specificity. Artificial intelligence represents the expansive vision of creating intelligent computational systems across diverse domains, while providing the primary practical mechanism enabling that vision through data-driven algorithms. That machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence—that ML serves as AI’s most powerful implementation method—clarifies technology selection and implementation strategy.
Rather than competing alternatives, AI and machine learning function as complementary technologies where machine learning algorithms power modern artificial intelligence systems across healthcare, finance, transportation, entertainment, and countless other industries. As data volumes expand and computational capabilities advance, these technologies will continue converging, increasingly becoming synonymous with practical artificial intelligence deployment. Organizations seeking competitive advantage must grasp these differences, recognizing when to deploy traditional artificial intelligence approaches versus leveraging data-adaptive capabilities for optimal results in their specific operational contexts.