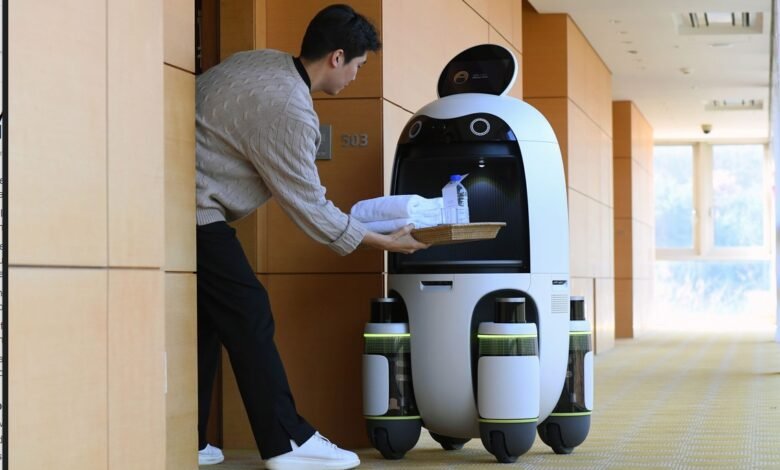
The landscape of customer service is undergoing a profound transformation as service robots emerge as powerful catalysts for change across multiple industries. From hotels deploying robotic concierges to restaurants utilizing automated waiters, these intelligent machines are redefining how businesses interact with their customers. Service robots represent more than just technological novelty—they embody a fundamental shift in service delivery that promises enhanced efficiency, reduced operational costs, and improved customer satisfaction.
As we navigate through 2025, the integration of robotics in customer experience has accelerated beyond predictions, driven by advances in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and human-robot interaction technologies. These sophisticated systems are no longer confined to futuristic concepts; they are actively reshaping customer service automation in hospitality, retail, healthcare, and logistics sectors. The COVID-19 pandemic acted as a catalyst, accelerating adoption as businesses sought contactless solutions to maintain service quality while ensuring safety.
The revolution brought by service robots extends beyond mere task automation. These intelligent systems offer 24/7 availability, consistent service quality, and the ability to handle repetitive tasks with precision, allowing human employees to focus on complex problem-solving and emotionally intelligence-requiring interactions. However, this transformation also raises important questions about the balance between automation and human touch, customer acceptance, and the future of employment in service industries.
The multifaceted impact of service robots on customer experience requires examining their applications, benefits, challenges, and the strategic considerations businesses must address. This comprehensive exploration reveals how organizations can leverage robotic technology to create competitive advantages while maintaining the human elements that remain irreplaceable in exceptional service delivery. As artificial intelligence in customer service continues evolving, businesses that strategically integrate these technologies position themselves at the forefront of innovation, ready to meet the expectations of increasingly tech-savvy consumers who demand both efficiency and personalized experiences.
Service Robots and Their Evolution
Service robots are sophisticated, system-based autonomous machines designed to interact, communicate, and deliver services to customers without constant human supervision. Unlike industrial robots confined to manufacturing floors, service robots operate in dynamic environments where they encounter unpredictable situations and interact directly with customers. These intelligent systems combine sensors, actuators, processing units, and increasingly sophisticated artificial intelligence to navigate spaces, recognize objects and people, understand commands, and execute service tasks.
The evolution of service robots traces back to early automation experiments, but recent advances in AI technology, computer vision, natural language processing, and machine learning have propelled them from experimental prototypes to commercially viable solutions. Modern service robots can understand context, adapt to changing circumstances, learn from interactions, and even display rudimentary social behaviors that make them more acceptable to customers. This technological maturity has opened doors for deployment across diverse sectors, including hospitality, healthcare, retail, and food service.
The classification of service robots spans several categories based on their functionality. Delivery robots transport items, meals, or medications within facilities. Reception robots handle check-ins, provide information, and authenticate identities. Cleaning robots maintain hygiene in hotels, hospitals, and public spaces. Telepresence robots enable remote interactions, particularly valuable in healthcare settings. Each category addresses specific operational needs while contributing to overall customer experience enhancement.
Integration of service robots into existing operations requires careful consideration of technical infrastructure, staff training, and customer readiness. Successful implementations recognize that these technologies complement rather than completely replace human workers, creating hybrid service models that leverage the strengths of both automation and human expertise.
The Impact on Customer Experience
The influence of service robots on customer experience presents a complex picture with both significant advantages and notable challenges. Research indicates that robotic service delivery can enhance efficiency, reduce wait times, and provide consistent service quality, particularly for routine and standardized tasks. Customers appreciate the novelty factor initially, and many find interactions with service robots efficient for straightforward transactions where emotional connection is less critical.
Service robots excel in environments requiring precision, speed, and tireless operation. In hotel settings, robots deliver room service without delays, ensuring items arrive at optimal temperature and condition. In healthcare facilities, service robots collect vital signs consistently and transport medications reliably, reducing human error risks. Retail environments benefit from robots that manage inventory, guide customers to products, and handle checkout processes seamlessly during peak periods.
However, the robot-human paradox reveals important limitations. Studies demonstrate that robot-provided services generally reduce positive emotions and behavioral intentions compared to human-provided services. Customers often perceive interactions with service robots as less warm, empathetic, and personalized. This emotional gap becomes particularly pronounced in services requiring compassion, complex problem-solving, or situations where customers seek a genuine human connection.
Interestingly, certain contexts favor robotic service over human interaction. In situations involving embarrassment—such as purchasing sensitive products or discussing private matters—customers sometimes prefer the anonymity and non-judgmental nature of robot interactions. Similarly, for simple, transactional services where efficiency outweighs relationship-building, service robots often meet or exceed customer expectations. The key lies in matching robot deployment to appropriate service scenarios while maintaining human availability for complex or emotionally sensitive interactions.
Applications Across Industries

Hospitality Industry Transformation
The hospitality industry has emerged as a pioneer in service robot adoption, with hotels, resorts, and restaurants deploying various robotic solutions to enhance guest experiences. Reception robots greet guests, handle check-ins, provide local information, and even authenticate identification documents using advanced scanning technology. These systems reduce wait times during busy periods while freeing human staff to address more complex guest needs and provide personalized recommendations.
Room service delivery robots navigate hotel corridors autonomously, transporting meals, amenities, and guest requests while avoiding obstacles and using elevators independently. Notable implementations include hotels where robots have become signature features, attracting tech-enthusiastic guests while delivering practical operational benefits. Restaurant service robots function as waiters, bussers, and food runners, carrying multiple dishes simultaneously and operating continuously without fatigue.
Housekeeping robots perform vacuuming, floor cleaning, and sanitization tasks, maintaining consistent cleanliness standards while allowing human staff to focus on detailed room preparation and guest-specific arrangements. The integration of service robots in hospitality creates opportunities for differentiation, operational efficiency, and contactless service options that have become increasingly valued by health-conscious travelers.
Retail Revolution
Retail service robots transform shopping experiences through inventory management, customer assistance, and checkout automation. These robots scan shelves continuously, identifying out-of-stock items, misplaced products, and pricing discrepancies, enabling real-time inventory accuracy that was previously impossible to maintain. Customer service robots guide shoppers to specific products, provide product information, and answer basic questions, particularly valuable in large retail spaces where human staff coverage is limited.
Self-service kiosks and robotic checkout systems expedite purchasing processes, reducing queue times and allowing customers to complete transactions at their own pace. Some retail environments deploy telepresence robots that connect remote customers with in-store associates, enabling personalized assistance for online shoppers who want expert guidance before purchasing. The data collection capabilities of retail robots provide valuable insights into shopping patterns, product popularity, and customer behavior that inform merchandising decisions.
Healthcare Innovation
Healthcare service robots address critical needs in medical facilities, including staff shortages, infection control, and consistent care delivery. Telepresence robots enable remote consultations, allowing specialists to interact with patients in distant locations or isolated environments without physical presence. Delivery robots transport medications, laboratory samples, linens, and supplies throughout hospitals, reducing staff workload and minimizing cross-contamination risks.
Patient assistance robots collect vital signs, remind patients about medications, and provide companionship for elderly or isolated individuals. Disinfection robots utilize UV-C light or chemical spraying to sanitize rooms and equipment thoroughly, crucial for infection prevention. Surgical robots, while distinct from service robots, represent the broader integration of robotics in healthcare that continues expanding into various care delivery aspects.
The implementation of service robots in healthcare must navigate regulatory requirements, privacy concerns, and the critical need for reliability in life-impacting situations. Successful deployments balance technological capabilities with the irreplaceable human elements of compassionate care and complex medical decision-making.
Key Benefits of Service Robot Implementation
Service robots deliver multiple advantages that justify investment and implementation efforts across industries. The most immediate benefit is operational efficiency—robots work continuously without breaks, fatigue, or inconsistency, handling repetitive tasks at constant quality levels. This reliability enables businesses to maintain service standards during peak periods, staff shortages, or overnight operations when human coverage is expensive or impractical.
Cost reduction represents another significant advantage. While initial investment in robotic systems can be substantial, the long-term operational savings through reduced labor costs, decreased errors, and improved resource utilization often justify the expenditure. Service robots don’t require salaries, benefits, or time off, and their maintenance costs are predictable and typically lower than cumulative human employee expenses for equivalent tasks.
Enhanced safety emerges as a critical benefit, particularly relevant following pandemic experiences. Robots minimize human contact requirements, reducing disease transmission risks while maintaining service continuity. They also handle potentially hazardous tasks like sanitization with dangerous chemicals or lifting heavy items that might cause human injury. In healthcare settings, service robots protect staff from exposure to infectious diseases while ensuring patients receive necessary care.
Data collection and analytics capabilities provide strategic advantages. Service robots continuously gather information about operations, customer interactions, service times, and environmental conditions. This data enables evidence-based decision-making, process optimization, and predictive maintenance that improves overall system performance. Businesses gain insights impossible to obtain through manual observation or sporadic sampling.
Scalability and flexibility allow organizations to adjust service capacity rapidly. Adding robot units is generally faster and more predictable than recruiting and training human staff, enabling businesses to respond quickly to demand fluctuations or expansion opportunities. Service robots can be reprogrammed for different tasks or locations, providing adaptability that traditional fixed automation lacks.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite their advantages, service robots face significant challenges that limit their effectiveness and adoption. Technical limitations remain prominent—robots struggle with unpredictable environments, complex social cues, and situations requiring creative problem-solving or emotional intelligence. Current AI technology, while advanced, cannot replicate human adaptability, empathy, or the nuance necessary for many customer interactions.
Customer acceptance varies considerably across demographics and contexts. While younger, tech-savvy customers often embrace robotic service, others find interactions uncomfortable, impersonal, or frustrating. The uncanny valley effect—discomfort with robots that appear almost but not quite human—can negatively impact customer perceptions. Cultural factors influence acceptance, with some societies more receptive to service robot integration than others.
Implementation costs present substantial barriers, particularly for small and medium-sized businesses. Beyond purchase prices, organizations must invest in infrastructure modifications, staff training, maintenance systems, and continuous software updates. The return on investment timeline can be lengthy, creating financial risks if technology becomes obsolete or customer acceptance proves lower than anticipated.
Employment concerns generate social and ethical debates. While proponents argue robots handle tasks humans prefer avoiding while creating new technical jobs, critics worry about the displacement of workers, particularly those in entry-level or low-skill positions heavily represented in service industries. Balancing automation benefits with social responsibility requires thoughtful approaches, including retraining programs and strategic workforce planning.
Maintenance and reliability issues can disrupt operations when robots malfunction. Unlike human workers who can improvise or assist each other, robot failures may require specialized technical support and replacement parts, potentially leaving service gaps. Ensuring robust backup systems and maintaining hybrid human-robot models helps mitigate these risks but adds complexity to operations management.
The Human-Robot Balance in Service Delivery
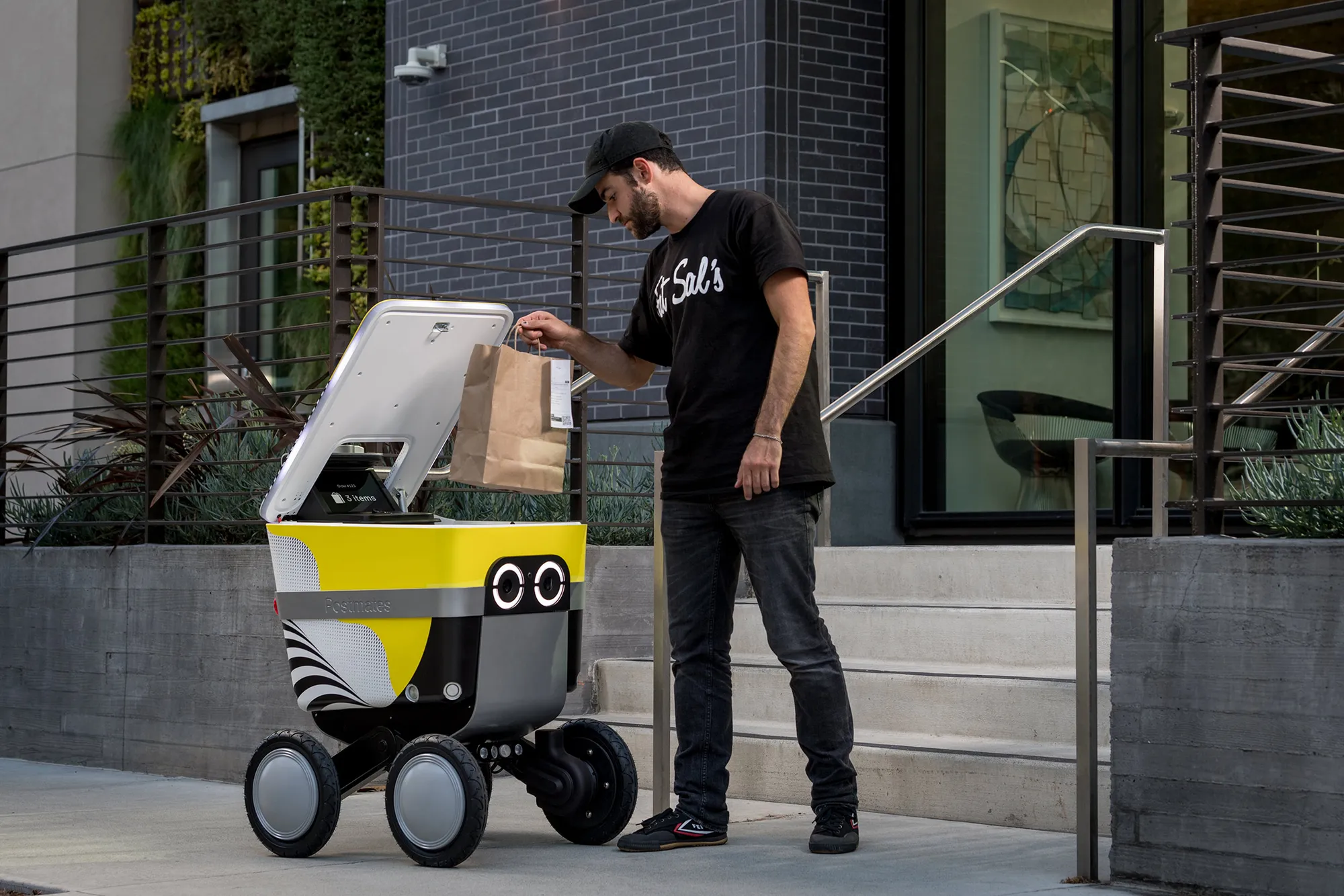

Creating optimal customer experiences requires a strategic balance between robotic automation and human service elements. The most successful implementations recognize that service robots and human employees have complementary strengths that, when properly integrated, deliver superior outcomes than either alone could achieve. This hybrid approach leverages robot efficiency for routine tasks while preserving human capacity for complex, emotional, and creative service aspects.
Task allocation should consider the nature of customer interactions. Standardized, predictable services like information provision, simple deliveries, or routine cleaning suit robotic execution well. Conversely, situations requiring empathy, negotiation, complaint resolution, or personalized recommendations demand human involvement. Clear protocols establishing when customers can escalate from robot to human assistance ensure satisfaction while maintaining operational efficiency.
Training human staff to work alongside service robots is essential. Employees need technical skills to supervise robot operations, troubleshoot minor issues, and seamlessly transition between automated and human service delivery. Additionally, staff must develop skills that differentiate human value—emotional intelligence, creative problem-solving, relationship building, and complex situation management—areas where robots cannot compete effectively.
Customer communication about robot roles sets appropriate expectations. Businesses should clearly indicate which services involve robots and provide easy options for human assistance when preferred. Transparency about robot capabilities and limitations prevents frustration while allowing customers to appreciate efficiency benefits. Some businesses position robots as novelty attractions that enhance brand identity rather than cost-cutting measures, improving customer receptiveness.
The future of service likely involves increasingly sophisticated human-robot collaboration where boundaries blur. AI-enhanced robots may handle broader ranges of interactions while systems enable seamless human intervention when needed. The goal remains delivering exceptional customer experiences that combine technological efficiency with irreplaceable human warmth.
Future Trends and Innovations
The trajectory of service robots points toward more sophisticated, capable, and integrated systems that fundamentally reshape customer service paradigms. Artificial intelligence advances will enable robots to understand context better, interpret emotional cues, engage in more natural conversations, and adapt behaviors based on individual customer preferences. Machine learning algorithms continuously improve robot performance through accumulated experience, making future systems progressively more effective.
Social robotics research focuses on making robot interactions more natural and comfortable. Developments in facial expressions, voice modulation, gesture recognition, and social protocol will help service robots navigate human interaction complexities more gracefully. However, developers must avoid the uncanny valley while creating systems that customers find approachable and trustworthy.
Multi-robot coordination systems will enable fleets of service robots working collaboratively, sharing information, and optimizing collective performance. In hotels, for example, robots could coordinate room service deliveries, cleaning schedules, and guest requests seamlessly, presenting to guests as a unified intelligent system rather than individual machines.
Integration with IoT ecosystems will expand robot capabilities dramatically. Connected service robots accessing building systems, customer databases, and environmental sensors can provide personalized, context-aware service that anticipates needs. Imagine hotel robots adjusting room temperatures before arrival, suggesting activities based on weather and preferences, or proactively offering assistance when sensors detect potential issues.
Sustainability considerations will influence robot design and deployment. Energy-efficient systems, recyclable materials, and robots that optimize resource usage align with environmental priorities while reducing operational costs. Service robots that extend building life through meticulous maintenance or reduce waste through precise inventory management contribute to broader sustainability goals.
Regulatory frameworks will evolve to address service robot deployment, establishing safety standards, liability protocols, privacy protections, and employment impact considerations. Industry standards will emerge defining acceptable robot behaviors, data handling practices, and human oversight requirements, providing clearer guidance for businesses considering implementation.
Strategic Implementation Considerations
Organizations contemplating service robot adoption must approach implementation strategically to maximize success probability and return on investment. A comprehensive needs assessment should precede any deployment, identifying specific operational challenges that robotic solutions might address effectively. Not every service task benefits from automation, and indiscriminate robot deployment wastes resources while potentially degrading customer experience.
Pilot programs allow organizations to test service robots in controlled environments before full-scale implementation. These trials reveal practical challenges, customer reactions, and operational impacts that inform refinement before broader deployment. Starting with clearly defined, limited applications reduces risk while building organizational knowledge and confidence.
Stakeholder engagement is critical—employees, customers, and management must understand robot roles, benefits, and limitations. Staff concerns about job security require transparent communication about how automation affects employment and what new opportunities emerge. Customer education helps set expectations and demonstrates value rather than presenting robots as impersonal cost-cutting measures.
Integration with existing systems demands careful planning. Service robots must work within current infrastructure, connect to relevant databases, and complement rather than disrupt established workflows. Technical compatibility, data security, and system redundancy require thorough evaluation to prevent implementation failures or security vulnerabilities.
Performance metrics should extend beyond operational efficiency to include customer satisfaction, employee impact, and return on investment. A comprehensive evaluation considers whether robot implementation achieves strategic objectives beyond simply reducing labor costs. Continuous monitoring and adjustment optimize robot performance and identify opportunities for expanded or modified deployment.
More Read: Robotics in Healthcare, Surgical Robots, and Patient Care Systems
Conclusion
Service robots are fundamentally transforming customer experience across hospitality, retail, healthcare, and numerous other industries, offering unprecedented efficiency, consistency, and operational capabilities. While these intelligent systems deliver clear benefits, including cost reduction, enhanced safety, and 24/7 availability, successful implementation requires a strategic balance between automation and irreplaceable human service elements.
The challenges of customer acceptance, technical limitations, and employment concerns demand thoughtful approaches that leverage robotic strengths for routine tasks while preserving human capacity for complex, emotional interactions. As AI technology advances and service robots become increasingly sophisticated, organizations that strategically integrate these systems while maintaining a customer-centric focus will lead the next evolution of service delivery, creating experiences that combine technological efficiency with the warmth and adaptability only humans provide. The future belongs not to robots replacing humans, but to intelligent collaboration that elevates customer service to new heights of effectiveness and satisfaction.