Machine Learning Frameworks Compared: TensorFlow vs PyTorch
Compare TensorFlow vs PyTorch deep learning frameworks. Explore key differences, performance, ease of use, and which ML framework is best.

In the rapidly evolving landscape of artificial intelligence and machine learning, selecting the right machine learning framework has become one of the most critical decisions for developers, data scientists, and AI engineers. Two names dominate this space: TensorFlow and PyTorch, both of which have revolutionized how we design, train, and deploy deep learning models. Since their inception, these deep learning frameworks have become the go-to tools for organizations ranging from startups to Fortune 500 companies, powering applications like natural language processing, computer vision, and generative AI.
TensorFlow, developed by Google Brain and released in 2015, was designed as a comprehensive, production-grade machine learning platform for handling scalable workflows across enterprises. PyTorch, launched by Facebook’s AI Research lab in 2016, emerged as a research-focused alternative emphasizing flexibility and ease of use. Today, both frameworks have matured significantly, with PyTorch commanding approximately 55% of the research community adoption in Q3 2025, while TensorFlow maintains robust presence in enterprise production environments with roughly 38% market share.
The decision between TensorFlow vs PyTorch isn’t merely about performance metrics or syntax preferences—it’s fundamentally about your project requirements, team expertise, and deployment strategy. Whether you’re building a prototype for academic research or deploying mission-critical AI systems, these AI frameworks offer distinct advantages. This comprehensive comparison explores the architectural differences, performance benchmarks, community ecosystems, and practical considerations that will help you choose the best neural network framework for your specific needs. By the end of this article, you’ll have clarity on which machine learning tool aligns with your project goals.
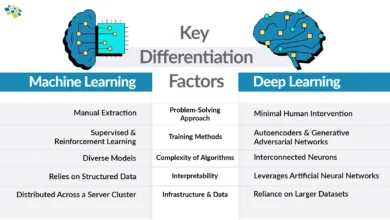
Machine Learning Frameworks
- Machine learning frameworks are sophisticated software libraries that provide pre-built components, tools, and interfaces to simplify the development of complex algorithms. These deep learning libraries abstract away the mathematical complexity underlying AI models, enabling developers to focus on architecture design and optimization rather than low-level implementations. Machine learning frameworks serve as the backbone of modern artificial intelligence, offering everything from data preprocessing utilities to model deployment solutions.
- TensorFlow and PyTorch represent two fundamentally different philosophies in framework design. TensorFlow uses a comprehensive ecosystem approach, bundling tools like TensorFlow Serving for production deployment, TensorBoard for visualization, and TensorFlow Lite for mobile applications. PyTorch, conversely, emphasizes modularity and flexibility, allowing developers to integrate third-party libraries like DeepSpeed for distributed training. These deep learning frameworks mean recognizing that both solve similar problems through different architectural paradigms that influence everything from debugging experiences to deployment pipelines.
TensorFlow: The Enterprise Deep Learning Framework
TensorFlow stands as one of the most widely adopted deep learning frameworks in enterprise settings, developed by Google and backed by exceptional documentation and community support. This machine learning platform was engineered specifically for production-scale deployments, making it the preferred choice for organizations requiring robustness, scalability, and enterprise-grade reliability. TensorFlow integrates seamlessly with Google Cloud services, offering native TPU support that delivers superior efficiency for large-scale training operations.
Core Architecture and Computation Model
TensorFlow originally employed static computation graphs, meaning the entire model architecture must be defined before computation occurs. This approach, while initially inflexible, allowed for substantial optimization opportunities at execution time. However, with TensorFlow 2.x, the framework introduced eager execution, enabling more intuitive, Pythonic code patterns similar to PyTorch’s approach. The tf.function decorator in TensorFlow converts Python functions into optimized static graphs, offering developers flexibility during development while maintaining performance during production deployment.
The framework’s core unit is the tensor, an n-dimensional arrays that flow through computational graphs. This design paradigm, while powerful, requires NumPy arrays and careful attention to tensor dimensions—a learning curve that can challenge newcomers. Despite improvements in TensorFlow 2.x, the framework maintains steeper cognitive demands compared to PyTorch for developers new to machine learning frameworks.
Production Deployment and Enterprise Tooling
- TensorFlow Serving emerges as the killer feature for production environments. This dedicated C++ serving system handles inference requests with exceptional efficiency, supporting model versioning, A/B testing, and zero-downtime updates across distributed clusters. Organizations like Netflix, Uber, and Twitter leverage TensorFlow Serving to power real-time recommendations and content personalization systems processing millions of requests daily.
- TensorBoard, integrated throughout the TensorFlow ecosystem, provides remarkable visualization capabilities for monitoring training metrics, analyzing model graphs, and debugging computational issues. TensorFlow Lite enables deployment on mobile and edge devices, while TensorFlow.js brings machine learning capabilities to web browsers. These comprehensive tools make TensorFlow the architecture of choice when production machine learning systems require enterprise-grade monitoring and deployment infrastructure.
Ecosystem and Integration
The TensorFlow ecosystem extends far beyond the core framework. Keras, originally a standalone deep learning library, is now integrated as TensorFlow’s high-level API, providing intuitive interfaces for sequential and functional model building. TensorFlow Hub offers pre-trained models for transfer learning, while TensorFlow Datasets provides standardized data loading pipelines. This comprehensive ecosystem reduces integration friction when building end-to-end machine learning solutions.
PyTorch: The Research and Flexibility Champion
PyTorch has become synonymous with cutting-edge deep learning research, dominating academic institutions and winning developer loyalty through intuitive design and exceptional debugging experiences. Developed by Meta (formerly Facebook) and now a Linux Foundation project, PyTorch prioritizes developer experience and flexibility, making it the preferred neural network framework for researchers prototyping novel architectures. The framework’s dynamic computation graph approach enables researchers to implement complex, non-standard architectures with unprecedented ease.
Dynamic Computation Graphs and Flexibility
PyTorch’s defining characteristic is its dynamic computation graph system, where the computational architecture is constructed at runtime rather than defined beforehand. This dynamic graph approach feels natural to Python developers, as operations execute immediately with results available instantaneously. Debugging becomes straightforward—you can insert standard Python print statements and use Python debuggers directly within training loops, dramatically accelerating the research iteration cycle.
This flexibility proves invaluable when implementing attention mechanisms, graph neural networks, or any architecture requiring conditional logic within forward passes. Researchers pushing the boundaries of artificial intelligence consistently choose PyTorch because the framework adapts to their algorithmic innovations rather than forcing compromises to fit a predefined execution model.
Intuitive API Design
PyTorch’s API design philosophy emphasizes clarity and conventionality. The torch.nn module provides building blocks—layers, activations, loss functions—that read intuitively to developers familiar with standard neural network concepts. Custom layers can be implemented by simply extending nn. Module and defining forward methods, an approach that feels far more Pythonic than equivalent TensorFlow implementations.
The optimizer ecosystem in PyTorch, including Adam, SGD, and AdamW variants, provides straightforward parameter update mechanisms with minimal configuration complexity. This simplicity accelerates experimentation, allowing researchers to focus on algorithmic innovations rather than wrestling with framework abstractions.
Community and Research Leadership
The PyTorch community has become the gravitational center for machine learning research. Major breakthroughs in transformer architectures, diffusion models, and large language models predominantly utilize PyTorch implementations. The Hugging Face transformers library, which democratized access to state-of-the-art models, is built on PyTorch, creating powerful network effects that reinforce the framework’s research dominance.
PyTorch Lightning provides an opinionated, higher-level abstraction layer that organizes training code without sacrificing the framework’s flexibility, appealing to developers seeking structure without losing control. This ecosystem diversity means PyTorch users can choose their desired abstraction level—from low-level tensor operations to high-level training templates.
Performance Comparison: Inference and Training Speed
When comparing TensorFlow vs PyTorch performance, the differences prove less dramatic than popular discourse suggests. Both frameworks achieve comparable inference latency on production hardware when properly optimized. TensorFlow’s static graph optimization sometimes provides marginal advantages for inference workloads, typically 5-15% improvements depending on specific architectures and hardware configurations.
Training performance depends heavily on implementation details. TensorFlow’s XLA (Accelerated Linear Algebra) compiler can deliver significant speedups for certain operations through aggressive graph-level optimizations. PyTorch’s native CUDA support and emerging TorchScript compilation capabilities provide competitive performance for most scenarios. For transformer training on TPUs, TensorFlow demonstrates consistent advantages, while PyTorch excels with distributed GPU training through frameworks like DeepSpeed and Fairseq.
Distributed training represents a critical performance domain. PyTorch’s DistributedDataParallel proves straightforward to implement and highly efficient across multiple GPUs and nodes. TensorFlow’s distributed training strategies offer greater flexibility but require deeper framework knowledge. For large-scale models exceeding single-machine capabilities, both frameworks achieve comparable scaling efficiency.
Ease of Learning and Development Experience
- PyTorch consistently ranks higher in developer satisfaction surveys regarding ease of learning. The framework’s imperative programming model aligns naturally with Python conventions, reducing cognitive overhead for newcomers. Learning PyTorch typically requires 1-2 weeks for developers with Python experience to achieve productive capability in building custom models.
- TensorFlow’s learning curve steepens considerably. The static graph paradigm, while ultimately powerful, requires conceptual leaps for developers from procedural programming backgrounds. Debugging TensorFlow code often demands a deeper of symbolic computation, session management (in TensorFlow 1.x), and tensor shape inference. Most developers require 3-4 weeks to develop proficiency comparable to early PyTorch users.
For teams prioritizing rapid prototyping and research agility, PyTorch’s lower barrier to entry translates directly to faster time-to-insight and more experimental iterations. For organizations with experienced machine learning engineers and production-focused goals, TensorFlow’s steeper learning curve represents an acceptable investment in exchange for production infrastructure benefits.
Production Deployment and Scalability
- TensorFlow shines brightest in production environments serving millions of daily requests. TensorFlow Serving’s battle-tested architecture handles model versioning, canary deployments, and serving multiple models simultaneously with minimal latency variance. Organizations operating massive recommendation systems, content ranking platforms, and real-time prediction services depend on TensorFlow’s production infrastructure.
- PyTorch production deployment, while historically underdeveloped, has matured substantially. TorchServe, built collaboratively between Meta and AWS, provides containerized model serving with reasonable performance and operational simplicity. The ONNX (Open Neural Network Exchange) format enables deploying PyTorch models across diverse inference engines, reducing cloud provider lock-in. Many organizations successfully deploy PyTorch to production through frameworks like FastAPI and containerized services.
The distinction reflects different design priorities rather than capability gaps. TensorFlow prioritizes production infrastructure as first-class framework components, while PyTorch delegates deployment concerns to specialized tools. Both approaches work at scale; the choice reflects operational preferences and existing cloud infrastructure.
Community Support and Ecosystem
- PyTorch’s open-source community has become more vibrant than TensorFlow’s, measured by GitHub contributions, Stack Overflow activity, and an emerging library ecosystem. Hundreds of specialized libraries—PyTorch Geometric for graph neural networks, PyTorch Lightning for structured training, Kornia for computer vision—extend PyTorch’s capabilities through community innovation.
- TensorFlow’s community, while substantial, shows signs of relative stagnation. Official documentation excels, but community contributions and third-party extensions develop at a slower pace. This reflects both PyTorch’s rise and TensorFlow’s strategic refocus toward Google Cloud integration rather than general-purpose ecosystem expansion.
For researchers and practitioners seeking cutting-edge implementations of novel architectures, PyTorch’s ecosystem advantage becomes decisive. Most recent papers released code in PyTorch rather than TensorFlow, creating positive feedback loops where community momentum reinforces framework preference.
Enterprise Requirements and Production Considerations
Enterprise organizations evaluating TensorFlow vs PyTorch must assess infrastructure requirements beyond raw capabilities. TensorFlow’s seamless Google Cloud integration proves valuable for organizations already committed to GCP. Native TPU support provides unmatched efficiency for appropriate workloads. Existing TensorFlow deployments create organizational inertia toward framework continuation.
PyTorch’s neutral positioning between cloud providers offers advantages for multi-cloud strategies. The framework’s simpler model format and smaller serialized model sizes reduce storage and bandwidth costs. Organizations emphasizing research agility and rapid model iteration increasingly select PyTorch despite acknowledging TensorFlow’s superior production infrastructure.
Mid-market and enterprise organizations typically adopt a pragmatic hybrid approach: PyTorch for research and prototyping, transitioning validated models to TensorFlow for production deployment. This strategy leverages each framework’s strengths while managing organizational risk and operational complexity.
More Read: What Is Transfer Learning and When Should You Use It?
Conclusion
The TensorFlow vs PyTorch decision fundamentally reflects prioritization between rapid research iteration and production infrastructure maturity. PyTorch dominates modern machine learning research, offering superior developer experience, intuitive APIs, and exceptional flexibility for algorithmic innovation. The dynamic computation graph paradigm enables researchers to implement novel architectures effortlessly, explaining PyTorch’s commanding 55% adoption share in academic institutions. TensorFlow, conversely, remains the gold standard for enterprise production deployments, providing unmatched infrastructure for serving millions of daily predictions at scale.
Google’s comprehensive ecosystem—TensorFlow Serving, TensorBoard, Keras—delivers production capabilities that organizations deploying mission-critical machine learning systems consistently depend upon. Rather than declaring a universal winner, sophisticated development teams recognize that both machine learning frameworks excel within their respective domains. The optimal choice depends on your specific requirements: choose PyTorch for research projects, rapid prototyping, and teams prioritizing developer experience; select TensorFlow for enterprise production systems, Google Cloud integration, and organizations requiring robust serving infrastructure. As both frameworks continue evolving—PyTorch strengthening production capabilities while TensorFlow improves ease of use—the practical differences narrow further, ultimately making either framework a defensible choice for serious machine learning development.