The revolution of smart home IoT devices has transformed how we interact with our living spaces, offering unprecedented convenience, energy efficiency, and security. As we navigate through 2025, the smart home technology landscape has evolved significantly, with the global connected home market projected to exceed $174 billion. Whether you’re a first-time buyer or looking to optimize your existing setup, knowing how to properly configure and manage your IoT home automation system is crucial for maximizing its potential.
Smart Home IoT Devices encompass everything from intelligent thermostats and lighting systems to advanced security cameras and voice-activated assistants. These connected devices communicate seamlessly through your home network, creating an ecosystem that learns your preferences and adapts to your lifestyle. However, the journey from purchasing your first smart device to building a fully integrated smart home requires careful planning, proper setup procedures, and ongoing optimization.
This comprehensive guide walks you through every aspect of Smart Home IoT Devices, from selecting the right devices and establishing a robust network infrastructure to implementing security measures and creating advanced automation routines. You’ll discover how to choose compatible devices, optimize your wireless connectivity, troubleshoot common issues, and protect your smart home from potential vulnerabilities. We’ll explore the essential components of a modern smart home ecosystem, including smart hubs, sensors, actuators, and control interfaces.
The complexity of IoT device integration can seem overwhelming at first, but with the right approach, you can create a smart home that genuinely enhances your daily life. We’ll demystify technical jargon, provide step-by-step instructions, and share expert tips that ensure your home automation system operates efficiently and securely. Whether you’re interested in voice control, smartphone management, or creating sophisticated automation scenes, this guide provides the knowledge you need to succeed.
By the end of this article, you’ll have mastered the fundamentals of smart home technology, equipped with practical strategies for setup, optimization, and long-term maintenance. Let’s embark on this journey to transform your house into an intelligent, responsive, and efficient smart home that serves your unique needs and preferences.
Smart Home IoT Technology
What Are Smart Home IoT Devices
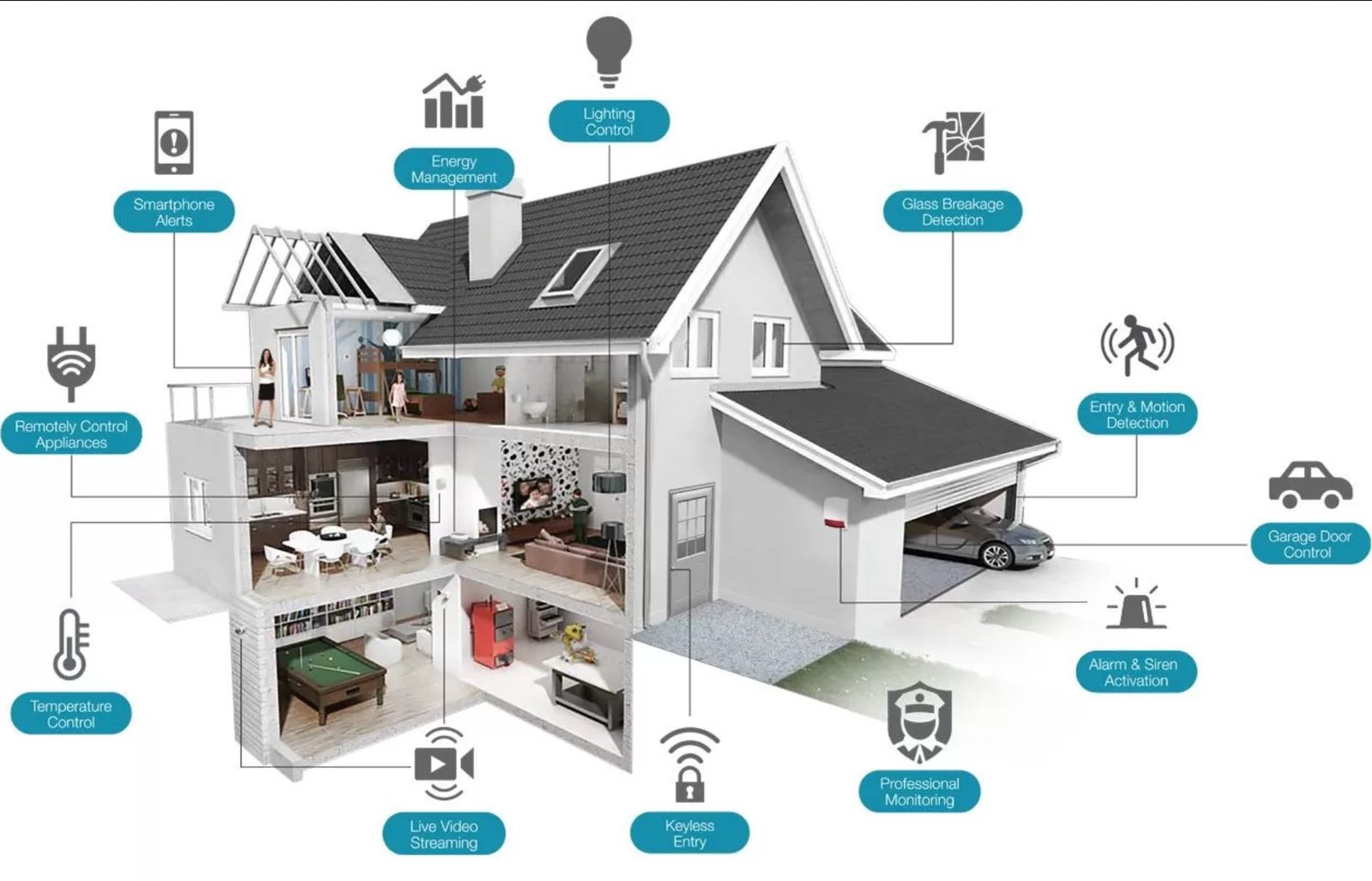
Smart home IoT devices are internet-connected appliances and systems that can be monitored, controlled, and automated remotely through smartphone applications, voice commands, or automated routines. These intelligent devices leverage the Internet of Things (IoT) framework to communicate with each other and with users, creating a cohesive ecosystem that responds to environmental changes and user preferences. The core functionality of IoT technology relies on sensors that collect data, processors that analyze information, and actuators that execute commands based on programmed logic or user inputs.
The architecture of Smart Home IoT Devices typically includes several layers: the device layer (physical hardware), the network layer (communication protocols), the platform layer (cloud services and local hubs), and the application layer (user interfaces). Modern IoT devices utilize various communication standards, including Wi-Fi, Zigbee, Z-Wave, Bluetooth, and Thread, each offering distinct advantages in terms of range, power consumption, and data transmission capabilities. These protocols are essential for building a reliable smart home network that operates efficiently without interference or connectivity issues.
Benefits of IoT Home Automation
Implementing home automation through IoT devices delivers substantial benefits across multiple dimensions of daily living. Energy efficiency stands as one of the most compelling advantages, with smart thermostats capable of reducing heating and cooling costs by up to 23% through intelligent temperature management and occupancy detection. Smart lighting systems automatically adjust brightness based on natural light availability and occupancy, while smart plugs enable scheduling and remote control of energy-consuming appliances, collectively reducing electricity consumption significantly.
Enhanced security represents another critical benefit of smart home technology. Connected security cameras, smart doorbells, and intelligent locks provide real-time monitoring and access control, allowing homeowners to verify visitors, grant temporary access to guests, and receive instant alerts about suspicious activity. The integration of motion sensors, door/window sensors, and smart alarms creates comprehensive security layers that protect against intrusions, fire, water damage, and other emergencies.
Convenience and comfort improvements through IoT automation fundamentally change how we interact with our homes. Voice-activated controls enable hands-free operation of lights, entertainment systems, and appliances. Automated routines like “Good Morning” can simultaneously adjust temperature, open blinds, start coffee makers, and provide weather updates with a single command. Smart Home IoT Devices learn user patterns over time, anticipating needs and adjusting settings proactively to maintain optimal comfort levels throughout the day.
Essential Smart Home IoT Devices for Beginners
Smart Speakers and Hubs
Smart speakers serve as the central command center for most smart home ecosystems, providing voice control capabilities and acting as communication hubs for other connected devices. Popular options include Amazon Echo with Alexa, Google Nest speakers with Google Assistant, and Apple HomePod with Siri. These devices function as Smart Home IoT Devices, facilitating communication between devices using different protocols and enabling unified control through a single interface. When selecting a smart speaker, consider compatibility with your existing devices, the quality of voice recognition, audio performance, and the ecosystem’s available integrations.
The choice between different smart hub platforms significantly impacts your smart home’s functionality and expandability. Amazon Alexa boasts the largest selection of compatible devices and skills, offering extensive third-party integrations. Google Assistant excels in natural language processing and search capabilities, making it ideal for information queries and calendar management. Apple HomeKit prioritizes privacy and security, featuring local processing and encrypted communication, though with a more limited device selection. Many advanced users incorporate multiple hubs to leverage the strengths of each platform while maintaining interoperability through services like IFTTT or Home Assistant.
Smart Lighting Solutions
Smart lighting represents an ideal entry point into home automation due to its straightforward installation, immediate impact, and relatively low cost. Smart bulbs like Philips Hue, LIFX, and Wyze offer color-changing capabilities, dimming options, and scheduling features that traditional lighting cannot match. These bulbs connect directly to your Wi-Fi network or through dedicated bridges, allowing control via smartphone apps or voice commands. For existing light fixtures, smart switches provide an alternative solution, replacing traditional wall switches and enabling control of entire lighting circuits without replacing individual bulbs.
Advanced lighting automation extends beyond simple on/off control to include dynamic scenes that adjust color temperature throughout the day, mimicking natural sunlight patterns to support circadian rhythms. Motion-activated lighting enhances convenience in hallways, bathrooms, and closets while reducing energy waste. Integration with other Smart Home IoT Devices enables sophisticated automations—lights can flash when the doorbell rings, dim automatically when you start watching movies, or gradually brighten to simulate sunrise for gentle wake-ups. Proper placement of sensors and thoughtful scene configuration transforms lighting from a basic utility into an intelligent system that enhances ambiance, security, and energy efficiency.
Smart Thermostats
Smart thermostats represent one of the highest-ROI investments in home automation, combining significant energy savings with enhanced comfort control. Leading models from Nest, Ecobee, and Honeywell learn your temperature preferences and schedule, automatically adjusting heating and cooling to minimize energy consumption while maintaining comfort. These devices utilize occupancy sensors, smartphone location data, and weather forecasts to optimize HVAC operation, pre-heating or pre-cooling your home before arrival, and entering energy-saving modes when you’re away.
Installation of smart thermostats typically requires basic electrical knowledge, as most replace existing thermostats using standard wiring connections. However, some HVAC systems may require a common wire (C-wire) to provide continuous power, and incompatible systems might need additional adapters or professional installation. The learning period for adaptive thermostats typically spans 1-2 weeks, during which the device observes your manual adjustments and establishes baseline patterns. Advanced features include room sensors that balance temperatures across multiple zones, humidity control, air quality monitoring, and energy usage reports that identify optimization opportunities.
Smart Security Cameras
Smart security cameras provide comprehensive surveillance capabilities with features far exceeding traditional CCTV systems. Modern IoT cameras offer high-definition video recording, night vision, motion detection, two-way audio, and cloud storage options. Indoor cameras monitor interior spaces, nanny cams, and pets, while weatherproof outdoor models guard entry points and perimeter areas. The choice between wired and battery-powered cameras depends on installation preferences, with wired models offering continuous recording capability and battery-powered options providing flexible placement without electrical requirements.
Key considerations when selecting smart cameras include resolution quality (1080p minimum, 4K for critical areas), field of view (wider angles cover more area but may reduce detail), storage options (local SD cards versus cloud subscriptions), and integration with other smart home systems. Privacy features such as physical camera shutters, local processing, and end-to-end encryption address growing concerns about unauthorized access. Advanced capabilities like person detection, package detection, facial recognition, and activity zones reduce false alerts while ensuring notification of genuinely important events. Integration with smart locks and smart lighting creates comprehensive security automations that deter intruders and provide evidence if incidents occur.
Step-by-Step Smart Home Setup Process
Planning Your Smart Home Ecosystem
Successful smart home implementation begins with comprehensive planning that considers your goals, budget, existing infrastructure, and long-term scalability. Start by identifying pain points in your current home—areas where automation could improve convenience, security, or efficiency. Prioritize devices that address these needs while considering which smart home ecosystem (Amazon Alexa, Google Home, Apple HomeKit) aligns best with your existing technology preferences and device compatibility requirements. Create a phased implementation plan that begins with foundational devices like smart speakers and gradually expands to more complex integrations.
Budget allocation for Smart Home IoT Devices should balance immediate purchases with future expansion plans. Entry-level smart home setups can begin with $200-500, covering a smart speaker, several smart bulbs, and a smart plug or two. Intermediate setups ranging from $1,000 to $2,500 add smart thermostats, security cameras, and smart locks. Advanced installations exceeding $5,000 incorporate whole-home audio, comprehensive security systems, motorized shades, and professional-grade networking equipment. Research compatibility before purchasing—ensuring devices support common standards like Matter, Zigbee, or Z-Wave prevents integration headaches and enables future device additions without ecosystem lock-in.
Network Infrastructure Optimization
Robust wireless connectivity forms the foundation of reliable smart home operation. Your Wi-Fi network must provide consistent coverage throughout your home with sufficient bandwidth to support multiple connected devices streaming data simultaneously. For most homes, a modern Wi-Fi 6 router positioned centrally provides adequate coverage, but larger homes or those with challenging layouts benefit from mesh networking systems that use multiple access points to eliminate dead zones. Dedicate the 2.4GHz band to IoT devices requiring extended range and the 5GHz band to devices needing higher bandwidth.
Network security and device segregation are critical components of smart home infrastructure. Create a separate guest network specifically for IoT devices, isolating them from computers and smartphones that contain sensitive personal information. This network segmentation prevents compromised smart devices from accessing your primary devices while maintaining functionality. Configure your router with strong WPA3 encryption, disable WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup), change default administrator credentials, and enable automatic firmware updates. Many modern routers include IoT-specific security features such as device identification, vulnerability scanning, and automatic threat blocking that provide additional protection layers.
Device Installation and Configuration
Proper installation procedures ensure Smart Home IoT Devices function reliably and integrate seamlessly with your ecosystem. Begin by updating your smart hub or speaker firmware to the latest version, ensuring compatibility with new devices. Follow manufacturer installation instructions carefully, paying attention to placement recommendations—sensors need a clear line-of-sight to monitored areas, speakers should be positioned away from walls for optimal audio, and hubs require central locations for maximum wireless range. Most devices follow a similar setup pattern: power on the device, download the manufacturer’s app, create an account if required, connect the device to Wi-Fi, and integrate with your chosen smart home platform.
Device naming conventions and organization significantly impact long-term usability. Use descriptive, intuitive names that voice assistants can easily understand—”Living Room Lamp” works better than “Lamp 1” when issuing voice commands. Group devices logically by room or function, enabling control of multiple devices simultaneously with commands like “turn off the bedroom lights.” Configure automation triggers thoughtfully, starting with simple routines before progressing to complex scenarios. Test each automation thoroughly, adjusting timing, conditions, and actions until they reliably produce desired results. Document your setup, including device locations, network credentials, automation logic, and troubleshooting steps for future reference.
Integration and Automation Setup
Creating effective home automation routines transforms disconnected smart devices into a cohesive system that anticipates needs and responds intelligently. Start with time-based automations that execute at scheduled intervals—morning routines that gradually increase lighting and adjust temperature, evening routines that secure doors and activate outdoor lighting, and sleep routines that turn off devices and arm security systems. Progress to condition-based automations triggered by sensor inputs, such as motion-activated lighting, temperature-based HVAC adjustments, and door sensor alerts when you’re away from home.
Advanced automation leverages multiple devices working in concert to create sophisticated scenarios. A “Movie Mode” routine might dim lights, close motorized blinds, adjust room temperature, activate entertainment systems, and silence phone notifications with a single command. Location-based automations use smartphone GPS to trigger actions when you arrive or leave home, such as unlocking doors, adjusting thermostats, and activating welcome lighting. IFTTT (If This Then That) and similar automation platforms extend capabilities beyond individual ecosystems, connecting web services, smart devices, and online accounts to create cross-platform automations impossible within single-vendor solutions.
Smart Home Security and Privacy
Protecting Your IoT Network
Smart Home IoT Devices extend beyond physical devices to encompass comprehensive network protection against cyber threats. Change all default passwords immediately upon device installation, using unique, complex passwords for each device and account. Enable two-factor authentication wherever available, adding an additional security layer that protects accounts even if passwords are compromised. Regularly update device firmware, as manufacturers frequently release patches addressing newly discovered vulnerabilities. Configure automatic updates when possible, ensuring devices receive critical security fixes without manual intervention.
Implement network monitoring tools that provide visibility into connected devices and their communication patterns. Many routers include traffic analysis features that identify suspicious behavior, such as devices communicating with unexpected external servers or generating unusual data volumes. Consider upgrading to a router with built-in security features like intrusion detection, malware blocking, and vulnerability scanning. For users requiring maximum security, virtual LANs (VLANs) provide complete network segregation between device categories, preventing any communication between trusted computers and potentially vulnerable IoT devices while maintaining internet connectivity for both.
Data Privacy Best Practices
Managing data collection by smart home devices protects personal privacy while maintaining functionality. Review privacy policies for all devices, noting what data they collect, how it’s used, and with whom it’s shared. Disable unnecessary data collection features, such as voice recording retention, usage analytics, and targeted advertising. Many devices offer local processing options that analyze data on-device rather than uploading to manufacturer servers, significantly reducing privacy exposure while maintaining functionality.
Camera privacy deserves special attention, given its potential for invasive surveillance. Position cameras to monitor entry points and common areas while avoiding bedrooms, bathrooms, and other private spaces. Utilize privacy modes that disable recording during specific times or when household members are home. Enable activity zones that limit recording to specific areas within the camera’s field of view, reducing unnecessary footage collection. For maximum privacy, consider systems offering end-to-end encryption and local storage that keep video data entirely under your control without third-party access.
Regular Security Audits
Conducting periodic security reviews identifies vulnerabilities before they’re exploited. Quarterly audits should include checking for firmware updates, reviewing connected devices for unauthorized additions, verifying automation rules remain appropriate, and testing security systems to confirm proper operation. Annually, consider comprehensive assessments that examine network architecture, evaluate emerging security technologies, and update practices based on evolving threat landscapes.
Remove or reset devices no longer in use, as abandoned Smart Home IoT Devices present security risks without providing benefits. When selling or disposing of smart devices, perform factory resets to eliminate stored configurations and credentials. Review app permissions regularly, revoking access for apps no longer used or requiring excessive permissions relative to their functionality. Document your security configuration, including passwords (stored securely in a password manager), network settings, and device inventories, enabling quick restoration if issues occur while providing clarity about your smart home’s security posture.
Optimization and Troubleshooting
Maximizing Device Performance
Optimal smart home performance requires attention to device placement, network configuration, and routine maintenance. Position devices within an adequate range of your wireless network, using signal strength indicators in device apps to identify weak connections. For devices experiencing persistent connectivity issues, consider adding mesh network nodes, repositioning the router, or utilizing Wi-Fi extenders designed for IoT device support. Battery-powered devices benefit from strategic placement that balances functionality with power conservation—frequently triggered sensors consume batteries rapidly, while optimal placement reduces unnecessary activations.
Reduce network congestion by distributing devices across available wireless bands and channels. Most smart home devices operate on 2.4GHz Wi-Fi, which offers better range but only three non-overlapping channels, making interference common in dense residential areas. Use Wi-Fi analysis apps to identify the least congested channels and configure your router accordingly. For homes with numerous connected devices, consider upgrading to Wi-Fi 6 routers that handle high device counts more efficiently through technologies like OFDMA and Target Wake Time. Disable bandwidth-intensive features you don’t use, such as continuous video recording when motion-activated recording suffices.
Common Issues and Solutions
Connectivity problems represent the most frequent smart home frustration. When devices disconnect or fail to respond, systematically troubleshoot by verifying internet connectivity, restarting the affected device, checking for firmware updates, and ensuring the device remains within wireless range. Router reboots resolve many temporary issues caused by DHCP assignment conflicts or memory leaks. For persistent problems, check whether recent changes (new devices, moved furniture, or neighboring network changes) coincide with issues emerging.
Voice control malfunctions often stem from poor microphone placement, ambient noise interference, or unclear command phrasing. Position smart speakers away from noise sources like TVs and air vents while ensuring clear line-of-sight to typical user locations. Use consistent, clear commands that match the assistant’s expected syntax. If the assistant misunderstands commands frequently, retrain voice recognition through the device app or consider alternative invocation phrases. Automation failures typically result from incorrect trigger conditions, device offline status, or insufficient permissions—review automation logs available in most platforms to identify specific failure points.
Advanced Optimization Techniques
Power users can implement advanced strategies that enhance smart home reliability and capabilities beyond standard configurations. Local control systems like Home Assistant, OpenHAB, or Hubitat eliminate cloud dependencies, enabling faster response times and continued operation during internet outages. These platforms aggregate devices from multiple ecosystems, providing unified control and enabling automations impossible within single-vendor solutions. However, they require technical proficiency and ongoing maintenance, making them better suited for enthusiasts willing to invest time in configuration and troubleshooting.
Network quality-of-service (QoS) configurations prioritize smart home traffic, ensuring reliable device communication even when network bandwidth is constrained by video streaming or large downloads. Advanced routers enable QoS rules that guarantee minimum bandwidth allocations or prioritize specific devices. For ultimate reliability, consider adding uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) to critical devices like routers, hubs, and security systems, maintaining smart home operation during power outages. Implement automated backup systems that regularly save device configurations and automation rules, enabling quick restoration if devices require factory resets or replacement.
Future-Proofing Your Smart Home
Emerging Technologies and Standards
The smart home landscape continues evolving rapidly, with new technologies promising enhanced interoperability and capabilities. Matter, the newest universal smart home standard backed by major technology companies, enables devices from different manufacturers to work together seamlessly without requiring brand-specific hubs or bridges. This standard simplifies device setup, improves reliability, and ensures long-term compatibility as the industry consolidates around common protocols. When purchasing new devices, prioritize Matter-certified products that guarantee future compatibility even as manufacturers and platforms evolve.
Thread networking provides a robust mesh protocol specifically designed for low-power IoT devices, offering superior reliability and battery life compared to traditional Wi-Fi or Bluetooth connections. Devices utilizing Thread create self-healing networks where each device acts as a repeater, extending range and providing redundant communication paths. Artificial intelligence integration continues advancing, with smart home systems becoming more proactive in learning preferences, predicting needs, and optimizing operations autonomously. Edge computing capabilities enable sophisticated processing directly on devices, improving response times and reducing privacy concerns associated with cloud-dependent systems.
Scalability Considerations
Building a Smart Home IoT device that accommodates future growth requires thoughtful planning regarding both technical infrastructure and financial investment. Select ecosystems and devices that support open standards, avoiding proprietary solutions that lock you into specific manufacturers or platforms. Invest in a robust networking infrastructure that exceeds current needs, providing headroom for additional devices and increased data traffic. Consider how devices will integrate with future additions—purchasing products with extensive third-party integrations provides flexibility as your smart home expands.
Document your smart home configuration comprehensively, including network diagrams, device inventories, automation logic, and configuration backups. This documentation proves invaluable when troubleshooting issues, replacing devices, or expanding your system. Establish relationships with local smart home installers or online communities that provide support and advice as you navigate increasingly complex configurations. Budget for ongoing costs, including device replacements (battery-powered devices typically last 1-3 years), subscription services (cloud storage, professional monitoring), and periodic upgrades that maintain compatibility with evolving standards and technologies.
More Read: IoT Security Protecting Connected Devices from Cyber Threats
Conclusion
Mastering smart home IoT devices transforms your living space into an intelligent, responsive environment that enhances comfort, security, and efficiency. This comprehensive guide has explored every aspect of smart home setup, from fundamental IoT concepts and selecting appropriate devices to implementing robust security measures and creating sophisticated automations. Success in building an effective smart home requires careful planning, methodical installation, ongoing optimization, and commitment to security best practices.
By following the strategies outlined here—establishing strong network infrastructure, choosing compatible devices, implementing thoughtful automations, and maintaining vigilant security—you create a smart home that genuinely improves daily life while protecting privacy and data. As technology continues evolving with innovations like Matter standardization and AI-enhanced automation, your foundation in smart home principles ensures you can adapt and expand your system to leverage emerging capabilities. The investment in time and resources to properly configure your smart home ecosystem delivers lasting returns through energy savings, enhanced security, and the unparalleled convenience of a home that anticipates your needs and responds intelligently to your lifestyle.